Treatment of fungal diseases should be carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist.Incorrectly selected antifungal agents can lead only to temporary improvement without curing the disease itself.
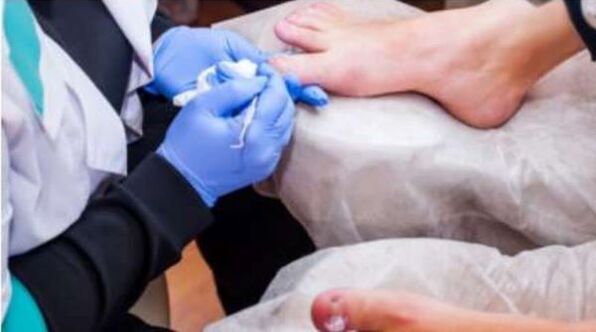
Treatment of fungal diseases should be carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist.In the case of self-medication, incorrectly selected antifungal agents can lead only to temporary improvement without curing the disease itself.
When choosing a treatment method, it is necessary to take into account the area and shape of the lesion, the degree of prevalence of the fungus, the presence of concomitant diseases and the age of the patient.
Antifungal drugs are divided into two types: for external and internal use.The external remedies themselves are effective only in the initial stages of the disease, so the treatment must be comprehensive: the fungus must be affected both from the outside and from the inside.
Internal preparations
For effective and safe treatment of fungal diseases with internal antifungal drugs, it is advisable to adhere to some rules:
- The diagnosis must be confirmed by a doctor.
- During treatment with internal antifungal drugs it is advisable to limit the intake of other drugs, except vital ones.
- Medicines should be used under the supervision of a doctor for a long time, until the fungus disappears completely.
- Check-ups should initially be carried out once every 2 weeks, then once a month.Control curettage - 6 months after the end of treatment.If a fungus is detected, a second course of treatment is required.
Currently, dermatologists consider pulse therapy the most effective and safe method of treatment, taking the drugs at long intervals.In some cases, a 1-week course of therapy is prescribed, followed by a 3-week break and then a new seven-day course of treatment.During administration, the drug accumulates in the body and continues to actively fight the infection in the following weeks.
The entire course of therapy usually lasts three months.However, after its completion, the medicine continues to act for a year, protecting against the reappearance of the fungus.This technique, on the one hand, allows the body to "rest" from taking drugs, on the other hand it does not exclude the possibility of taking other drugs, including antibiotics.Furthermore, the risk of recurrence is significantly reduced.
External preparations
When the nails are affected, not only internal drugs are used, but also topical drugs: nail polishes, peel-off patches and ointments (keratolytics).
Loceryl and Batrafen 5% are used as antifungal varnishes, which can penetrate into the deep layers of the nail and nail bed.Varnishes are applied to the nail with top saw (the affected areas of the nail surface can be removed using a nail file included with the varnish), clean and degreased nail (for example with alcohol).
Additionally, keratolytic ointments and patches can be used to remove the affected area of the nail.These products soften the nail, so they are easily and painlessly removed from the surface of the nail bed.Currently used patches contain urea or salicylic acid as a keratolytic component.Sometimes an antiseptic (quinozole, iodine) or a local antifungal agent, such as ketoconazole, is added to the patch.
A keratolytic patch is applied to the surface of the nail and covered with an adhesive plaster and a bandage.After 2-3 days, the affected areas are cleaned and the patch is reapplied.Procedures are performed daily until the affected nails are completely removed.The average duration of treatment is 6 months for fingernails and 9-12 months for toenails.
In addition, a special set for nail treatment is produced, which includes an ointment with both antifungal and keratolytic effects, a nail scraper and a plaster.
For fungal skin infections, topical creams are used, for example loceryl.The cream is applied daily to the affected areas.The average duration of treatment is 2-3 weeks;during treatment of feet - up to 6 weeks.
Treatment of contaminated objects (disinfection)
During and after treatment of a fungal infection, it is very important to disinfect everything that the fungus has come into contact with.Floors, walls, equipment of bathtubs, showers, bathrooms, as well as the patient's personal belongings: underwear, shoes, skin and nail care items must be disinfected.
The walls and bottom of the tub should be treated with a mixture of equal parts detergent and bleach or chloramine, diluted to a creamy consistency (the powder should be washed off after 30 minutes).You can also use a 5% solution of chloramine or bleach or a 3% solution of Lysol.
It is recommended to treat shoes with solutions of formaldehyde (25%) or acetic acid (40%).You should thoroughly clean the insoles and side areas of your shoes with a moistened swab.Then insert the swab into the toe of the shoe, and place the shoe in a hermetically sealed plastic bag for 24 hours.After using acetic acid or 25% formaldehyde solution, the shoes are ventilated or cleaned with ammonia to eliminate the odor.
Underwear, stockings, socks, tights can be disinfected by boiling for 15-20 minutes in a 2% sodium bicarbonate solution.Then they should be ironed with a hot iron.
Nail scissors are disinfected by dipping them in alcohol and then burning them on the flame of a burner.
Prevention
To prevent foot fungus infection, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- Use only your own shoes.
- Do not wear tight shoes, which retain a humid environment and expose the skin and nails to friction and microtraumas.
- Take care of your shoes;shoes must be well dried after wearing them.
- People who often visit saunas, swimming pools, baths, sports and gyms are advised to use local antifungal agents (ointments, creams, paints).
- Avoid porous carpets in the bathroom - they are difficult to wash and therefore provide an excellent haven for a variety of microorganisms, including fungi.



















